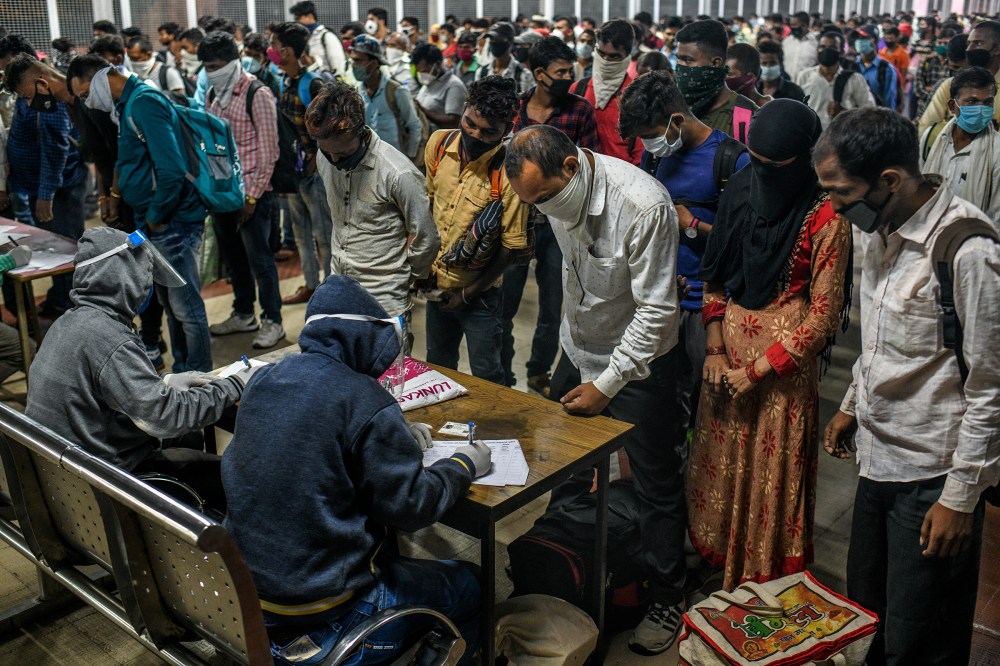
With a white handkerchief covering his mouth and nose, only Rajkumar Prajapati’s tired eyes were visible as he stood in line.
It was before sunrise on Aug. 5, but there were already hundreds of others waiting with him under fluorescent lights at the main railway station in Pune, an industrial city not far from Mumbai, where they had just disembarked from a train. Each person carried something: a cloth bundle, a backpack, a sack of grain. Every face was obscured by a mask, a towel or the edge of a sari. Like Prajapati, most in the line were workers returning to Pune from their families’ villages, where they had fled during the lockdown. Now, with mounting debts, they were back to look for work. When Prajapati got to the front of the line, officials took his details and stamped his hand with ink, signaling the need to self-isolate for seven days.

After Prime Minister Narendra Modi appeared on national television on March 24 to announce that India would go under lockdown to fight the coronavirus, Prajapati’s work as a plasterer for hire at construction sites around Pune quickly dried up. By June, his savings had run out and he, his wife and his brother left Pune for their village 942 miles away, where they could tend their family’s land to at least feed themselves. But by August, with their landlord asking for rent and the construction sites of Pune reopening, they had no option but to return to the city. “We might die from corona, but if there is nothing to eat we will die either way,” said Prajapati.
As the sun rose, he walked out of the station into Pune, the most infected city in the most infected state in all of India. As of Aug. 18, India has officially recorded more than 2.7 million cases of COVID-19, putting it third in the world behind the U.S. and Brazil. But India is on track to overtake them both. “I fully expect that at some point, unless things really change course, India will have more cases than any other place in the world,” says Dr. Ashish Jha, director of Harvard’s Global Health Institute. With a population of 1.3 billion, “there is a lot of room for exponential growth.”
Read More: India’s Coronavirus Death Toll Is Surging. Prime Minister Modi Is Easing Lockdown Anyway
The pandemic has already reshaped India beyond imagination. Its economy, which has grown every year for the past 40, was faltering even before the lockdown, and the International Monetary Fund now predicts it will shrink by 4.5% this year. Many of the hundreds of millions of people lifted out of extreme poverty by decades of growth are now at risk in more ways than one. Like Prajapati, large numbers had left their villages in recent years for new opportunities in India’s booming metropolises. But though their labor has propelled their nation to become the world’s fifth largest economy, many have been left destitute by the lockdown. Gaps in India’s welfare system meant millions of internal migrant workers couldn’t get government welfare payments or food. Hundreds died, and many more burned through the meager savings they had built up over years of work.
Now, with India’s economy reopening even as the virus shows no sign of slowing, economists are worried about how fast India can recover—and what happens to the poorest in the meantime. “The best-case scenario is two years of very deep economic decline,” says Jayati Ghosh, chair of the Centre for Economic Studies and Planning at Jawaharlal Nehru University in Delhi. “There are at least 100 million people just above the poverty line. All of them will fall below it.”
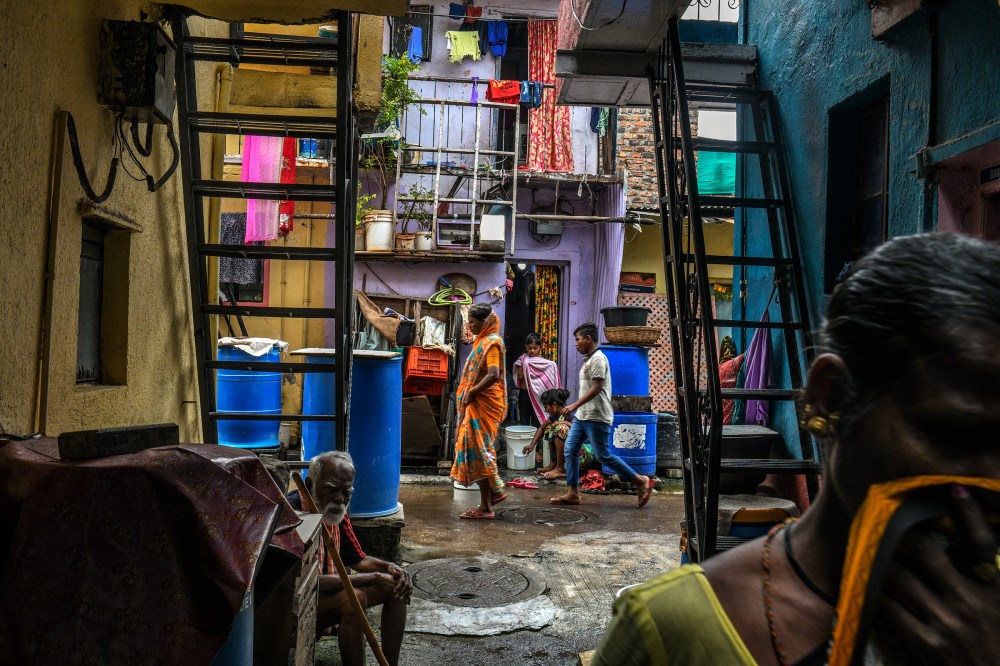
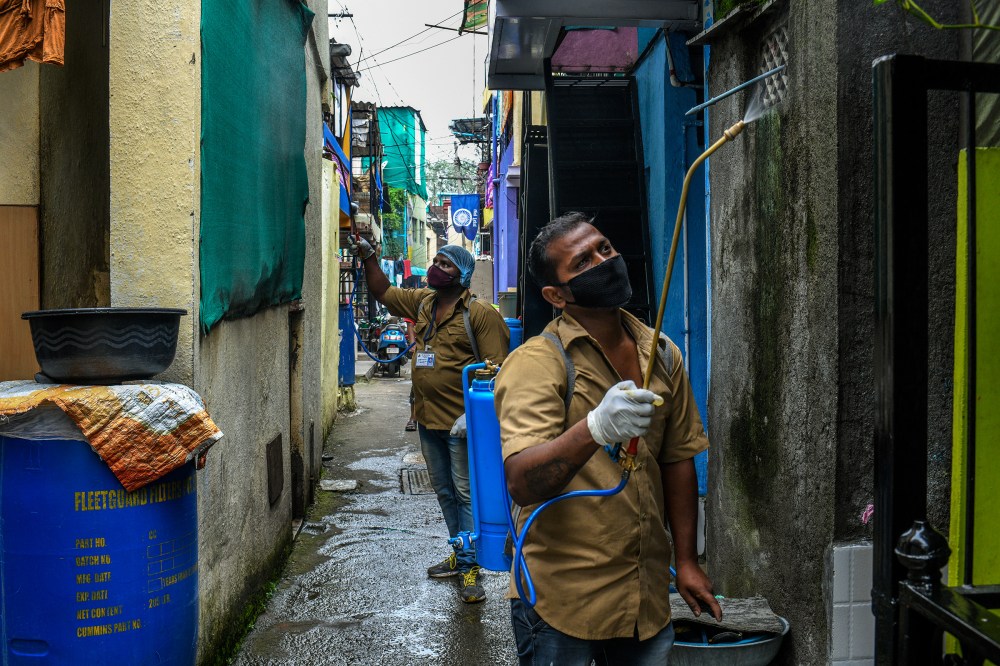



In some ways Prajapati, 35, was a lucky man. He has lived and worked in Pune since the age of 16, though like many laborers, he regularly sends money home to his village and returns every year to help with the harvest. Over the years, his remittances have helped his father build a four-room house. When the lockdown began, he even sent his family half of the $132 he had in savings. The $66 Prajapati had left was still more than many had at all, and enough to survive for three weeks. His landlord let him defer his rent payments. Two weeks into the lockdown, when Modi asked citizens in a video message to turn off their lights and light candles for nine minutes at 9 p.m. in a show of national solidarity, Prajapati was enthusiastic, lighting small oil lamps and placing them at shrines in his room and outside his door. “We were very happy to do it,” he said. “We thought that perhaps this will help with corona.”
Other migrant workers weren’t so enthusiastic. For those whose daily wages paid for their evening meals, the lockdown had an immediate and devastating effect. When factories and construction sites closed because of the pandemic, many bosses—who often provide their temporary employees with food and board—threw everyone out onto the streets. And because welfare is administered at a state level in India, migrant workers are ineligible for benefits like food rations anywhere other than in their home state. With no food or money, and with train and bus travel suspended, millions had no choice but to immediately set off on foot for their villages, some hundreds of miles away. By mid-May, 3,000 people had died from COVID-19, but at least 500 more had died from “distress deaths” including those due to hunger, road accidents and lack of access to medical facilities, according to a study by the Delhi-based Society for Social and Economic Research. “It was very clear there had been a complete lack of planning and thought to the implications of switching off the economy for the vast majority of Indian workers,” says Yamini Aiyar, president of the Centre for Policy Research, a Delhi think tank.
One migrant worker who decided to make the risky journey on foot was Tapos Mukhi, 25, who set off from Chiplun, a small town in the western state of Maharashtra, toward his village in the eastern state of Odisha, over 1,230 miles away. He had tried to work through the lockdown, but his boss held back his wages, saying he did not have money to pay him immediately. Mukhi took another job at a construction site in June, but after a month of lifting bricks and sacks of cement, a nail went through his foot, forcing him to take a day off. His supervisor called him lazy and told him to leave without the $140 he was owed. On Aug. 1, he walked for a day in the pouring monsoon rain with his wife and 3-year-old daughter, before a local activist arranged for a car to Pune. “We had traveled so far from our village to work,” said Mukhi, sitting on a bunk bed in a shelter in Pune, where activists from a Pune-based NGO had given him and his family train tickets. “But we didn’t get the money we were owed and we didn’t even get food. We have suffered a lot. Now we never want to leave the village again.”
Although Indian policymakers have long been aware of the extent to which the economy relies on informal migrant labor like Mukhi’s—there are an estimated 40 million people like him who regularly travel within the country for work—the lockdown brought this long invisible class of people into the national spotlight. “Something that caught everyone by surprise is how large our migrant labor force is, and how they fall between all the cracks in the social safety net,” says Arvind Subramanian, Modi’s former chief economic adviser, who left government in 2018. Modi was elected in 2014 after a campaign focused on solving India’s development problems, but under his watch economic growth slid from 8% in 2016 to 5% last year, while flagship projects, like making sure everyone in the country has a bank account, have hit roadblocks. “The truth is, India needs migration very badly,” Subramanian says. “It’s a source of dynamism and an escalator for lots of people to get out of poverty. But if you want to get that income improvement for the poor back, you need to make sure the social safety net works better for them.”
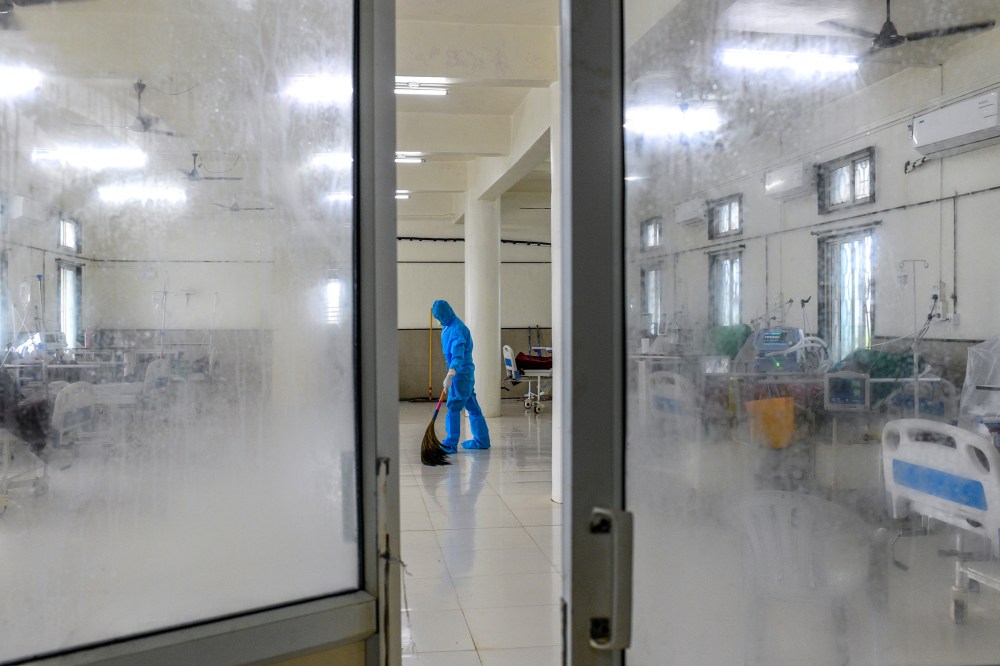
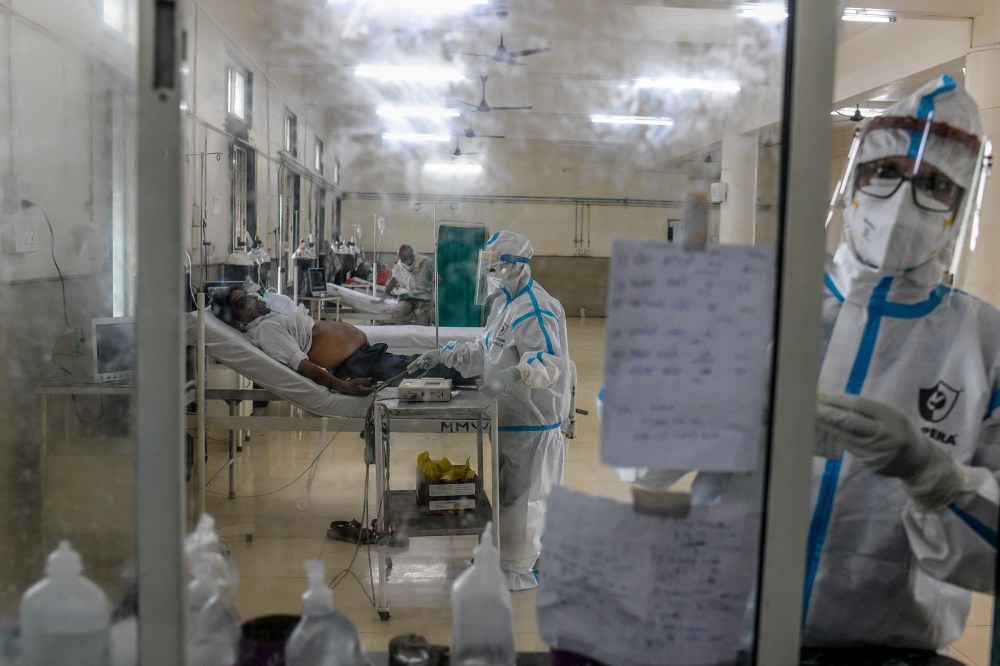
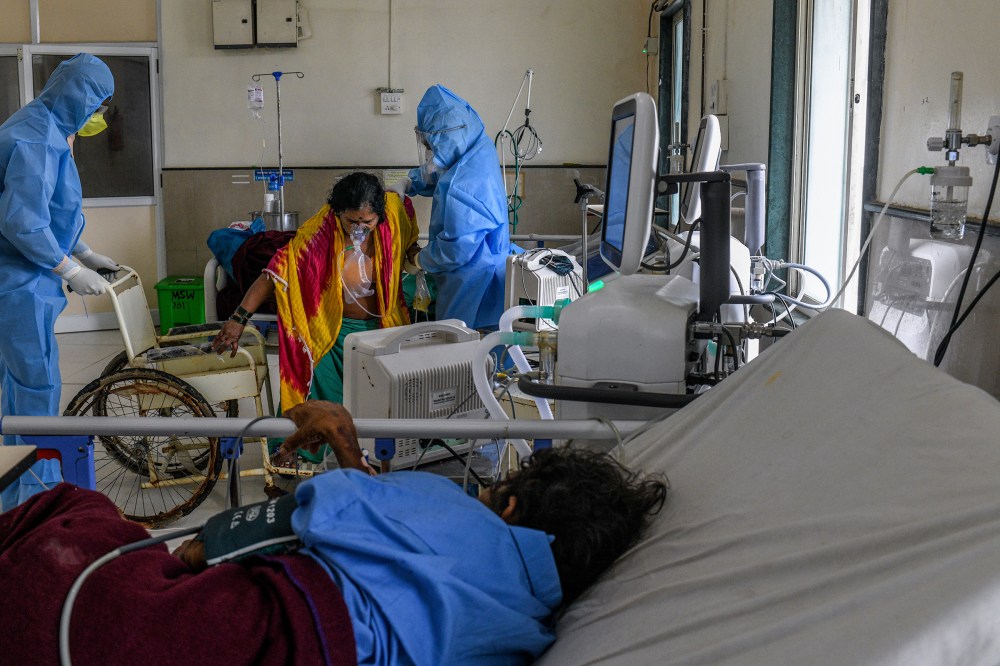

The wide-scale economic disruption caused by the lockdown has disproportionately affected women. Because 95% of employed women work in India’s informal economy, many lost their jobs, even as the burden remained on them to take care of household responsibilities. Many signed up for India’s rural employment scheme, which guarantees a set number of hours of unskilled manual labor. Others sold jewelry or took on debts to pay for meals. “The COVID situation multiplied the burden on women both as economic earners and as caregivers,” says Ravi Verma of the Delhi-based International Center for Research on Women. “They are the frontline defenders of the family.”
But the rural employment guarantee does not extend to urban areas. In Dharavi, a sprawling slum in Mumbai, Rameela Parmar worked as domestic help in three households before the lockdown. But the families told her to stop coming and held back her pay for the last four months. To support her own family, she was forced to take daily wage work painting earthen pots, breathing fumes that make her feel sick. “People have suffered more because of the lockdown than [because of] corona,” Parmar says. “There is no food and no work—that has hurt people more.”
Girls were hit hard too. For Ashwini Pawar, a bright-eyed 12-year-old, the pandemic meant the end of her childhood. Before the lockdown, she was an eighth-grade student who enjoyed school and wanted to be a teacher someday. But her parents were pushed into debt by months of unemployment, forcing her to join them in looking for daily wage work. “My school is shut right now,” said Pawar, clutching the corner of her shawl under a bridge in Pune where temporary workers come to seek jobs. “But even when it reopens I don’t think I will be able to go back.” She and her 13-year-old sister now spend their days at construction sites lifting bags of sand and bricks. “It’s like we’ve gone back 10 years or more in terms of gender-equality achievements,” says Nitya Rao, a gender and development professor who advises the U.N. on girls’ education.
In an attempt to stop the economic nosedive, Modi shifted his messaging in May. “Corona will remain a part of our lives for a long time,” he said in a televised address. “But at the same time, we cannot allow our lives to be confined only around corona.” He announced a relief package worth $260 billion, about 10% of the country’s GDP. But only a fraction of this came as extra handouts for the poor, with the majority instead devoted to tiding over businesses. In the televised speech announcing the package, Modi spoke repeatedly about making India a self-sufficient economy. It was this that made Prajapati lose hope in ever getting government support. “Modiji said that we have to become self-reliant,” he said, still referring to the Prime Minister with an honorific suffix. “What does that mean? That we can only depend on ourselves. The government has left us all alone.”
By the time the lockdown began to lift in June, Prajapati’s savings had run out. His government ID card listed his village address, so he was not able to access government food rations, and he found himself struggling to buy food for his family. Three times, he visited a public square where a local nonprofit was handing out meals. On June 6, he finally left Pune for his family’s village, Khazurhat. He had been forced to borrow from relatives the $76 for tickets for his wife, brother and himself. But having heard the stories of migrants making deadly journeys back, he was thankful to have found a safe way home.

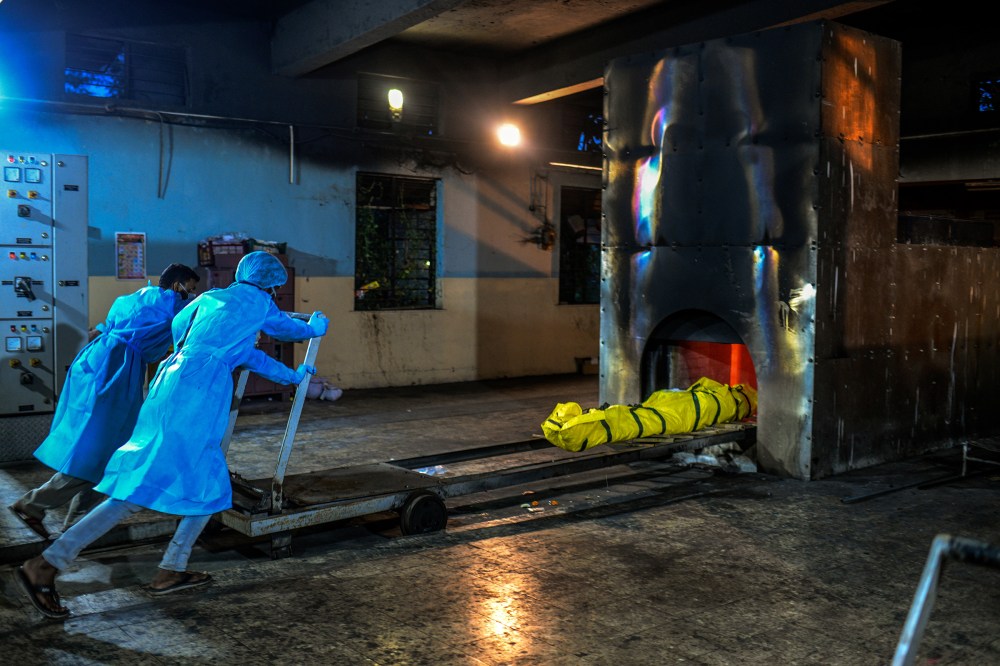
Meanwhile, the virus had been spreading across India, despite the lockdown. The first hot spots were India’s biggest cities. In Pune, Kashinath Kale, 44, was admitted to a public hospital with the virus on July 4, after waiting in line for nearly four hours. Doctors said he needed a bed with a ventilator, but none were available. His family searched in vain for six days, but no hospital could provide one. On July 11, he died in an ambulance on the way to a private hospital, where his family had finally located a bed in an intensive-care unit with a ventilator. “He knew he was going to die,” says Kale’s wife Sangeeta, holding a framed photograph of him. “He was in a lot of pain.”
By June, almost every day saw a new record for daily confirmed cases. And as COVID-19 moved from early hot spots in cities toward rural areas of the country where health care facilities are less well-equipped, public-health experts expressed concern, noting India has only 0.55 hospital beds per 1,000 people, far below Brazil’s 2.15 and the U.S.’s 2.80. “Much of India’s health infrastructure is only in urban areas,” says Ramanan Laxminarayan, director of the D.C.-based Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy. “As the pandemic unfolds it is moving into states which have very low levels of testing and rural areas where the public-health infrastructure is weak.”
Read More: India Is the World’s Second-Most Populous Country. Can It Handle the Coronavirus Outbreak?
When he arrived back in his village of Khazurhat, Prajapati’s neighbors were worried he might have been infected in Pune, so medical workers at the district hospital checked his temperature and asked if he had any symptoms. But he was not offered a test. “While testing has been getting better in India, it’s still nowhere near where it needs to be,” says Jha.
Nevertheless, Modi has repeatedly touted India’s low case fatality rate—the number of deaths as a percentage of the number of cases—as proof that India has a handle on the pandemic. (As of Aug. 17 the rate was 1.9%, compared with 3.1% in the U.S.) “The average fatality rate in our country has been quite low compared to the world … and it is a matter of satisfaction that it is constantly decreasing,” Modi said in a televised videoconference on Aug. 11. “This means that our efforts are proving effective.”

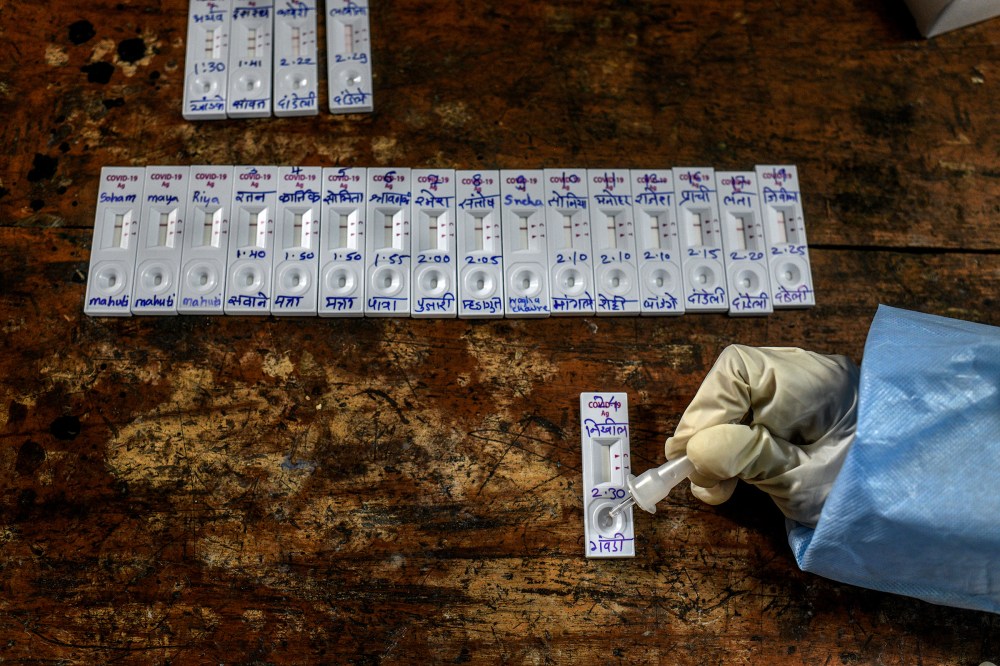

But experts say this language is dangerously misleading. “As long as your case numbers are increasing, your case fatality rate will continue to fall,” Jha says. When the virus is spreading exponentially as it is currently in India, he explains, cases increase sharply but deaths, which lag weeks behind, stay low, skewing the ratio to make it appear that a low percentage are dying. “No serious public-health person believes this is an important statistic.” On the contrary, Jha says, it might give people false optimism, increasing the risk of transmission.
Modi’s move to lock down the country in March was met with a surge in approval ratings; many Indians praised the move as strong and decisive. But while other foreign leaders’ lockdown honeymoons eventually gave way to popular resentment, Modi’s ratings remained stratospheric. In some recent polls, they topped 80%.
The reason has much to do with his wider political project, which critics see as an attempt to turn India from a multifaith constitutional democracy into an authoritarian, Hindu-supremacist state. Since winning re-election with a huge majority in May 2019, Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), the political wing of a much larger grouping of organizations whose stated mission is to turn India into a Hindu nation, has delivered on several long-held goals that excite its right-wing Hindu base at the expense of the country’s Muslim minority. (Hindus make up 80% of the population and Muslims 14%.) Last year the government revoked the autonomy of India’s only Muslim-majority state, Kashmir. And an opulent new temple is being built in Ayodhya—a site where many Hindus believe the deity Ram was born and where Hindu fundamentalists destroyed a mosque on the site in 1992. After decades of legal wrangling and political pressure from the BJP, in 2019 the Supreme Court finally ruled a temple could be built in its place. On Aug. 5, Modi attended a televised ceremony for the laying of the foundation stone.
Read More: The Battle for India’s Founding Ideals
Still, before the pandemic Modi was facing his most severe challenge yet, in the form of a monthslong nationwide protest movement. All over the country, citizens gathered at universities and public spaces, reading aloud the preamble of the Indian constitution, quoting Mohandas Gandhi and holding aloft the Indian tricolor. The protests began in December 2019 as resistance to a controversial law that would make it harder for Muslim immigrants from Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh, to gain Indian citizenship. They morphed into a wider pushback against the direction of the country under the BJP. In local Delhi elections in February, the BJP campaigned on a platform of crushing the protests but ended up losing seats. Soon after, riots broke out in the capital; 53 people were killed, 38 of them Muslims. (Hindus were also killed in the violence.) Police failed to intervene to stop Hindu mobs roaming around Muslim neighborhoods looking for people to kill, and in some cases joined mob attacks on Muslims themselves, according to a Human Rights Watch report.

“During those hundred days I thought India had changed forever,” says Harsh Mander, a prominent civil-rights activist and director of the Centre for Equity Studies, a Delhi think tank, of the three months of nationwide dissent from December to March. But the lockdown put an abrupt end to the protests. Since then, the government has ramped up its crackdown on dissent. In June, Mander was accused by Delhi police (who report to Modi’s interior minister, Amit Shah) of inciting the Delhi riots; in the charges against him, they quoted out of context portions of a speech he had made in December calling on protesters to continue Gandhi’s legacy of nonviolent resistance, making it sound instead like he was calling on them to be violent. Meanwhile, local BJP politician Kapil Mishra, who was filmed immediately before the riots giving Delhi police an ultimatum to clear the streets of protesters lest his supporters do it themselves, still walks free. “In my farthest imagination I couldn’t believe there would be this sort of repression,” Mander says.
Read More: ‘Hate Is Being Preached Openly Against Us.’ After Delhi Riots, Muslims in India Fear What’s Next
A pattern was emerging. Police have also arrested at least 11 other protest leaders, including Safoora Zargar, a 27-year-old Muslim student activist who organized peaceful protests. She was accused of inciting the Delhi riots and charged with murder under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act, a harsh anti-terrorism law that authorities used at least seven times during the lockdown to arrest activists or journalists. The law is described by Amnesty International as a “tool of harassment,” and by Zargar’s lawyer Ritesh Dubey, in an interview with TIME, as aimed at “criminalizing dissent.” As COVID-19 spread around the country, Zargar was kept in jail for two months, without bail, despite being 12 weeks pregnant at the time of her arrest. Restrictions in place to curb the spread of coronavirus, like not allowing lawyers to visit prisons, have also impacted protesters’ access to legal justice, Dubey says.
“The government used this health emergency to crush the largest popular movement this country has seen since independence,” Mander says. “The Indian Muslim has been turned into the enemy within. The economy has tanked, there is mass hunger, infections are rising and rising, but none of that matters. Modi has been forgiven for everything else. This normalization of hate is almost like a drug. In the intoxication of this drug, even hunger seems acceptable.”
Read More: It Was Already Dangerous to Be Muslim in India. Then Came the Coronavirus
Close to going hungry, Prajapati says the Modi administration has provided little relief for people like him. “If we have not gotten anything from the government, not even a sack of rice, then what can we say to them?” he says. “I don’t have any hope from the government.”
Still a change in government would be too much for Prajapati, a devout Hindu and a Modi supporter, who backs the construction of the temple of Ram in Ayodhya and cheered on the BJP when it revoked the autonomy of Kashmir. “There is no one else like Modi who we can put our faith in,” he says. “At least he has done some good things.”
Prajapati remained in Khazurhat from June until August, working his family’s acre of farmland where they grow rice, wheat, potatoes and mustard. But there was little other work available, and the yield from their farm was not sufficient to support the family. Now $267 in debt to employers and relatives, he decided to return to Pune along with his wife and brother. Worried about reports of rising cases in the city, his usually stoic father cried as he waved him off from the village. On his journey, Prajapati carried 44 lb. of wheat and 22 lb. of rice, which he hoped would feed his family until he could find construction work.
On the evening of his return, Prajapati cleaned his home, cooked dinner from what he had carried back from the village, and began calling contractors to look for work. The pandemic had set him back at least a year, he said, and it would take him even longer to pay back the money he owed. The stamp on his hand he’d received at the station, stating that he was to self-quarantine for seven days, had already faded. Prajapati was planning to work as soon as he could. “Whether the lockdown continues or not, whatever happens we have to live here and earn some money,” he said. “We have to find a way to survive.”
—With reporting by Madeline Roache/London
